

^C timed ~]# dig +short connection timed out no servers could be reachedĪlso the logs can be found in CloudWatch logs: Neither target was accessible after the rules were created.
Set-cookie: YSC=PuFCQ_QHLcQ Domain=. Path=/ Secure HttpOnly SameSite=none Set-cookie: GPS=1 Domain=. Expires=Tue, 3 01:42:54 GMT Path=/ Secure HttpOnly P3p: CP="This is not a P3P policy! See for more info." Strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000 īefore created the rules, I was able to curl, and dig ~]# curl -I Ĭache-control: no-cache, no-store, max-age=0, must-revalidate

Add stateful rule to deny https/http traffic to domain.Add stateless rule to drop all protocols to 8.8.8.8/32.Here are two simple tests that I have done to show you how it work: Network Firewall supports both stateless and stateful policies. Second Example: Workload VPC uses Egress VPC for Internet outbound traffics (centralised model). I have done two AWS Network Firewall deployments recently, which I think are the typical use cases.įirst example: Workload VPC uses its own Network Firewall for Internet Ingress and Egress (distributed model).

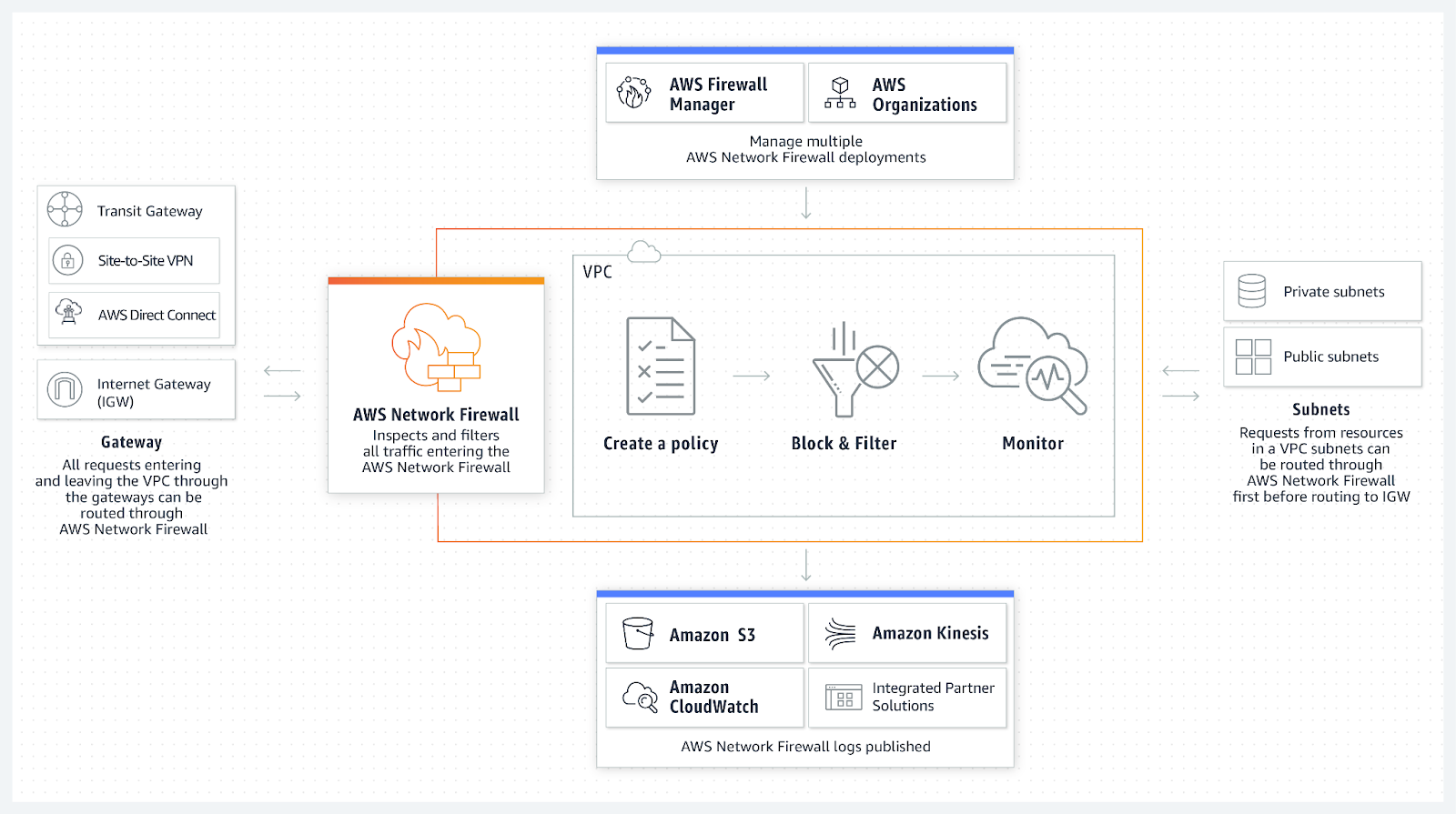
Different use cases have different deployment models. There are quite a few use cases for AWS Network Firewall, e.g VPC-to-VPC inspection, VPC-to-Onprem/VPN inspecton, VPC-to-Internet inspection. WAF (Web Application Firewall) and Shield protects frontend resources (ELB, CloudFound, API Gateway).NACL (Network Access Control List) protects subnets.Security group protects computing resources (EC2, Lambda, RDS…).AWS Network Firewall is a high-available and scalable firewall service that provides network protections for VPC, which is a supplement to the existing security services.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
